[ad_1]

A lot of the world is roofed in oceans, that are sadly extremely polluted. One of many methods to fight the mounds of waste present in these very delicate ecosystems – particularly round coral reefs – is to make use of robots to grasp the cleanup. Nonetheless, current underwater robots are principally cumbersome with inflexible our bodies, unable to discover and pattern in complicated and unstructured environments, and are noisy as a consequence of electrical motors or hydraulic pumps. For a extra appropriate design, scientists on the Max Planck Institute for Clever Programs (MPI-IS) in Stuttgart appeared to nature for inspiration. They configured a jellyfish-inspired, versatile, energy-efficient and almost noise-free robotic the dimensions of a hand. Jellyfish-Bot is a collaboration between the Bodily Intelligence and Robotic Supplies departments at MPI-IS. “A Versatile Jellyfish-like Robotic Platform for Effective Underwater Propulsion and Manipulation” was printed in Science Advances.
To construct the robotic, the staff used electrohydraulic actuators by which electrical energy flows. The actuators function synthetic muscle tissue which energy the robotic. Surrounding these muscle tissue are air cushions in addition to mushy and inflexible parts which stabilize the robotic and make it waterproof. This fashion, the excessive voltage operating by the actuators can not contact the encircling water. An influence provide periodically supplies electrical energy by skinny wires, inflicting the muscle tissue to contract and increase. This enables the robotic to swim gracefully and to create swirls beneath its physique.
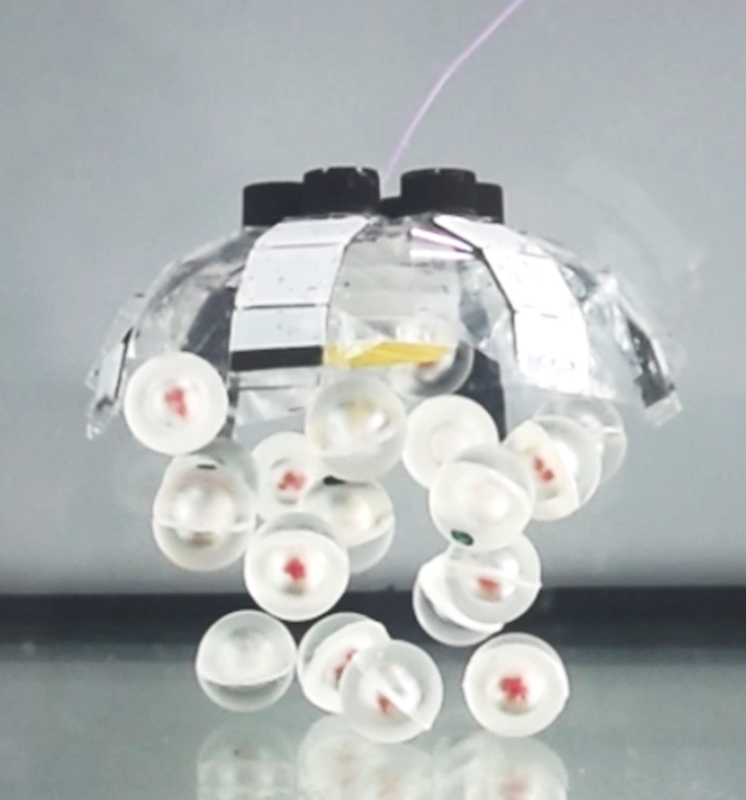
“When a jellyfish swims upwards, it may lure objects alongside its path because it creates currents round its physique. On this manner, it may additionally gather vitamins. Our robotic, too, circulates the water round it. This operate is beneficial in accumulating objects akin to waste particles. It may possibly then transport the litter to the floor, the place it may later be recycled. Additionally it is in a position to gather fragile organic samples akin to fish eggs. In the meantime, there is no such thing as a unfavorable impression on the encircling surroundings. The interplay with aquatic species is mild and almost noise-free”, Tianlu Wang explains. He’s a postdoc within the Bodily Intelligence Division at MPI-IS and first creator of the publication.
His co-author Hyeong-Joon Joo from the Robotic Supplies Division continues: “70% of marine litter is estimated to sink to the seabed. Plastics make up greater than 60% of this litter, taking a whole lot of years to degrade. Subsequently, we noticed an pressing have to develop a robotic to control objects akin to litter and transport it upwards. We hope that underwater robots may someday help in cleansing up our oceans.”
Jellyfish-Bots are able to transferring and trapping objects with out bodily contact, working both alone or with a number of together. Every robotic works sooner than different comparable innovations, reaching a velocity of as much as 6.1 cm/s. Furthermore, Jellyfish-Bot solely requires a low enter energy of round 100 mW. And it’s protected for people and fish ought to the polymer materials insulating the robotic someday be torn aside. In the meantime, the noise from the robotic can’t be distinguished from background ranges. On this manner Jellyfish-Bot interacts gently with its surroundings with out disturbing it – very similar to its pure counterpart.
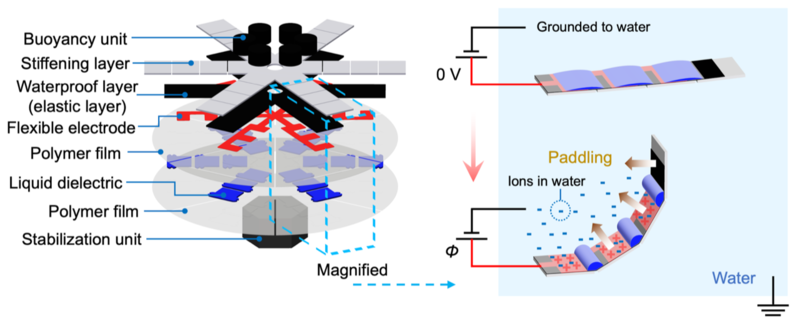
The robotic consists of a number of layers: some stiffen the robotic, others serve to maintain it afloat or insulate it. An extra polymer layer capabilities as a floating pores and skin. Electrically powered synthetic muscle tissue often called HASELs are embedded into the center of the totally different layers. HASELs are liquid dielectric-filled plastic pouches which can be partially coated by electrodes. Making use of a excessive voltage throughout an electrode prices it positively, whereas surrounding water is charged negatively. This generates a power between positively-charged electrode and negatively-charged water that pushes the oil contained in the pouches forwards and backwards, inflicting the pouches to contract and chill out – resembling an actual muscle. HASELs can maintain the excessive electrical stresses generated by the charged electrodes and are protected in opposition to water by an insulating layer. That is vital, as HASEL muscle tissue had been by no means earlier than used to construct an underwater robotic.
Step one was to develop Jellyfish-Bot with one electrode with six fingers or arms. Within the second step, the staff divided the one electrode into separated teams to independently actuate them.
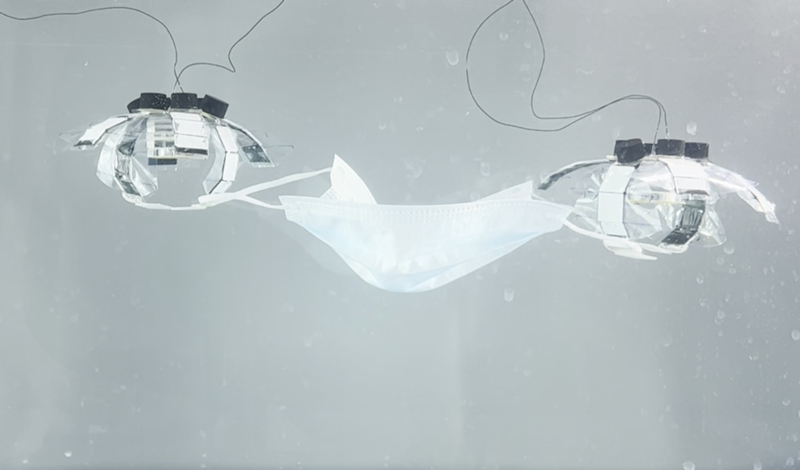
“We achieved greedy objects by making 4 of the arms operate as a propeller, and the opposite two as a gripper. Or we actuated solely a subset of the arms, so as to steer the robotic in numerous instructions. We additionally appeared into how we are able to function a collective of a number of robots. As an example, we took two robots and allow them to choose up a masks, which could be very tough for a single robotic alone. Two robots may also cooperate in carrying heavy hundreds. Nonetheless, at this level, our Jellyfish-Bot wants a wire. This can be a disadvantage if we actually wish to use it someday within the ocean”, Hyeong-Joon Joo says.
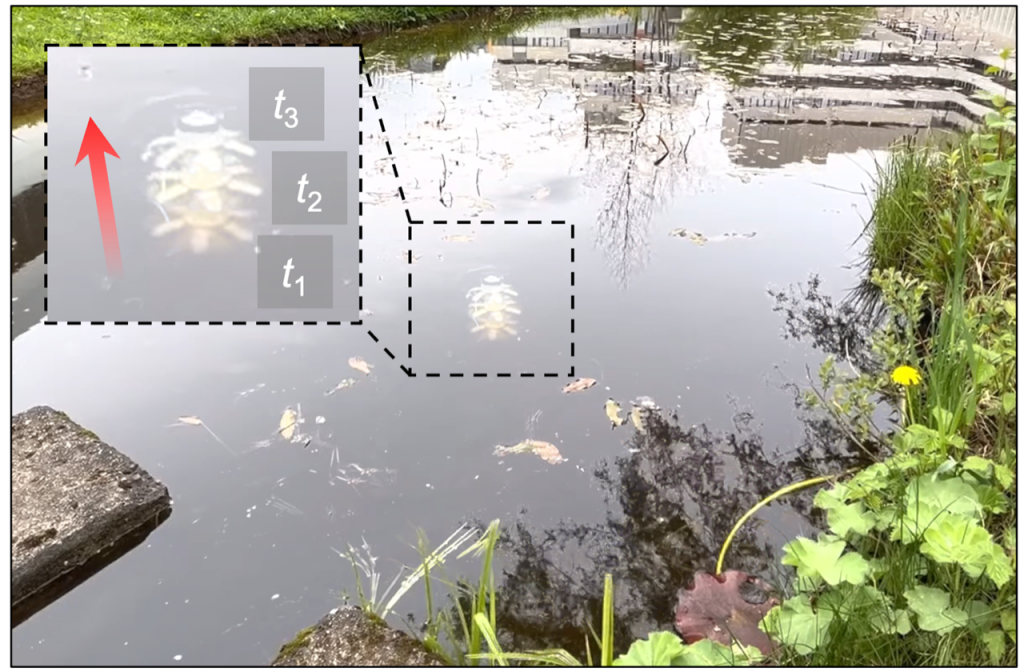
Maybe wires powering robots will quickly be a factor of the previous. “We goal to develop wi-fi robots. Fortunately, we now have achieved step one in direction of this aim. We now have integrated all of the purposeful modules just like the battery and wi-fi communication components in order to allow future wi-fi manipulation”, Tianlu Wang continues. The staff hooked up a buoyancy unit on the prime of the robotic and a battery and microcontroller to the underside. They then took their invention for a swim within the pond of the Max Planck Stuttgart campus, and will efficiently steer it alongside. To date, nonetheless, they might not direct the wi-fi robotic to alter course and swim the opposite manner.
Understanding the staff, it received’t take lengthy to realize this aim.
tags: bio-inspired

Max Planck Institute for Clever Programs
‘s aim is to analyze and perceive the organizing rules of clever programs and the underlying perception-action-learning loop.
[ad_2]
Source link



