[ad_1]
Editor’s notice: This put up was up to date on November 17 after the announcement of the Gordon Bell prize winners.
The winner of the Gordon Bell particular prize for prime efficiency computing-based COVID-19 analysis has taught large language models (LLMs) a brand new lingo — gene sequences — that may unlock insights in genomics, epidemiology and protein engineering.
Published in October, the groundbreaking work is a collaboration by greater than two dozen educational and business researchers from Argonne Nationwide Laboratory, NVIDIA, the College of Chicago and others.
The analysis workforce skilled an LLM to trace genetic mutations and predict variants of concern in SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19. Whereas most LLMs utilized to biology thus far have been skilled on datasets of small molecules or proteins, this undertaking is likely one of the first fashions skilled on uncooked nucleotide sequences — the smallest items of DNA and RNA.
“We hypothesized that transferring from protein-level to gene-level information may assist us construct higher fashions to grasp COVID variants,” mentioned Arvind Ramanathan, computational biologist at Argonne, who led the undertaking. “By coaching our mannequin to trace the complete genome and all of the modifications that seem in its evolution, we will make higher predictions about not simply COVID, however any illness with sufficient genomic information.”
The Gordon Bell awards, considered the Nobel Prize of excessive efficiency computing, have been offered on the SC22 convention by the Affiliation for Computing Equipment, which represents round 100,000 computing specialists worldwide. Since 2020, the group has awarded a particular prize for excellent analysis that advances the understanding of COVID with HPC.
Coaching LLMs on a 4-Letter Language
LLMs have lengthy been skilled on human languages, which normally comprise a pair dozen letters that may be organized into tens of hundreds of phrases, and joined collectively into longer sentences and paragraphs. The language of biology, then again, has solely 4 letters representing nucleotides — A, T, G and C in DNA, or A, U, G and C in RNA — organized into totally different sequences as genes.
Whereas fewer letters might seem to be an easier problem for AI, language fashions for biology are literally much more difficult. That’s as a result of the genome — made up of over 3 billion nucleotides in people, and about 30,000 nucleotides in coronaviruses — is tough to interrupt down into distinct, significant items.
“In terms of understanding the code of life, a serious problem is that the sequencing data within the genome is sort of huge,” Ramanathan mentioned. “The which means of a nucleotide sequence might be affected by one other sequence that’s a lot additional away than the following sentence or paragraph can be in human textual content. It may attain over the equal of chapters in a e-book.”
NVIDIA collaborators on the undertaking designed a hierarchical diffusion technique that enabled the LLM to deal with lengthy strings of round 1,500 nucleotides as in the event that they have been sentences.
“Customary language fashions have hassle producing coherent lengthy sequences and studying the underlying distribution of various variants,” mentioned paper co-author Anima Anandkumar, senior director of AI analysis at NVIDIA and Bren professor within the computing + mathematical sciences division at Caltech. “We developed a diffusion mannequin that operates at a better stage of element that permits us to generate lifelike variants and seize higher statistics.”
Predicting COVID Variants of Concern
Utilizing open-source information from the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Useful resource Heart, the workforce first pretrained its LLM on greater than 110 million gene sequences from prokaryotes, that are single-celled organisms like micro organism. It then fine-tuned the mannequin utilizing 1.5 million high-quality genome sequences for the COVID virus.
By pretraining on a broader dataset, the researchers additionally ensured their mannequin may generalize to different prediction duties in future tasks — making it one of many first whole-genome-scale fashions with this functionality.
As soon as fine-tuned on COVID information, the LLM was capable of distinguish between genome sequences of the virus’ variants. It was additionally capable of generate its personal nucleotide sequences, predicting potential mutations of the COVID genome that would assist scientists anticipate future variants of concern.
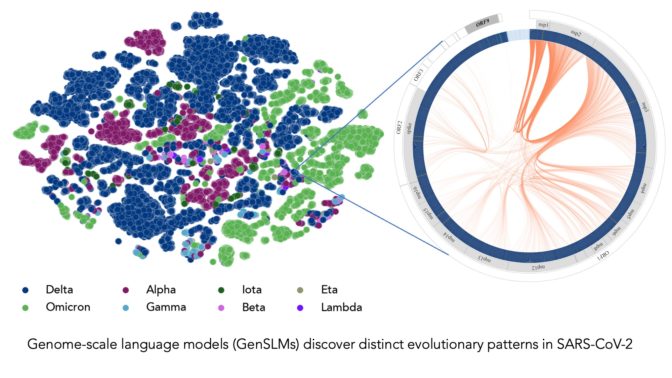
“Most researchers have been monitoring mutations within the spike protein of the COVID virus, particularly the area that binds with human cells,” Ramanathan mentioned. “However there are different proteins within the viral genome that undergo frequent mutations and are necessary to grasp.”
The mannequin may additionally combine with well-liked protein-structure-prediction fashions like AlphaFold and OpenFold, the paper acknowledged, serving to researchers simulate viral construction and examine how genetic mutations influence a virus’ potential to contaminate its host. OpenFold is likely one of the pretrained language fashions included within the NVIDIA BioNeMo LLM service for builders making use of LLMs to digital biology and chemistry functions.
Supercharging AI Coaching With GPU-Accelerated Supercomputers
The workforce developed its AI fashions on supercomputers powered by NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs — together with Argonne’s Polaris, the U.S. Division of Vitality’s Perlmutter, and NVIDIA’s in-house Selene system. By scaling as much as these highly effective methods, they achieved efficiency of greater than 1,500 exaflops in coaching runs, creating the biggest organic language fashions thus far.
“We’re working with fashions as we speak which have as much as 25 billion parameters, and we anticipate this to considerably enhance sooner or later,” mentioned Ramanathan. “The mannequin measurement, the genetic sequence lengths and the quantity of coaching information wanted means we actually want the computational complexity supplied by supercomputers with hundreds of GPUs.”
The researchers estimate that coaching a model of their mannequin with 2.5 billion parameters took over a month on round 4,000 GPUs. The workforce, which was already investigating LLMs for biology, spent about 4 months on the undertaking earlier than publicly releasing the paper and code. The GitHub web page consists of directions for different researchers to run the mannequin on Polaris and Perlmutter.
The NVIDIA BioNeMo framework, out there in early access on the NVIDIA NGC hub for GPU-optimized software program, helps researchers scaling massive biomolecular language fashions throughout a number of GPUs. A part of the NVIDIA Clara Discovery assortment of drug discovery instruments, the framework will assist chemistry, protein, DNA and RNA information codecs.
Discover NVIDIA at SC22 and watch a replay of the particular deal with beneath:
Picture at prime represents COVID strains sequenced by the researchers’ LLM. Every dot is color-coded by COVID variant. Picture courtesy of Argonne Nationwide Laboratory’s Bharat Kale, Max Zvyagin and Michael E. Papka.
[ad_2]
Source link



