[ad_1]

Emotionally clever’ robots may enhance their interactions with individuals. Andriy Onufriyenko/Second by way of Getty Pictures
By Ramana Vinjamuri (Assistant Professor of Laptop Science and Electrical Engineering, College of Maryland, Baltimore County)
Robots are machines that may sense the surroundings and use that data to carry out an motion. You could find them almost in every single place in industrialized societies as we speak. There are family robots that vacuum flooring and warehouse robots that pack and ship items. Lab robots check a whole lot of medical samples a day. Education robots assist academics by appearing as one-on-one tutors, assistants and dialogue facilitators. And medical robotics composed of prosthetic limbs can allow somebody to understand and decide up objects with their ideas.
Determining how people and robots can collaborate to successfully perform duties collectively is a quickly rising space of curiosity to the scientists and engineers that design robots in addition to the individuals who will use them. For profitable collaboration between people and robots, communication is essential.
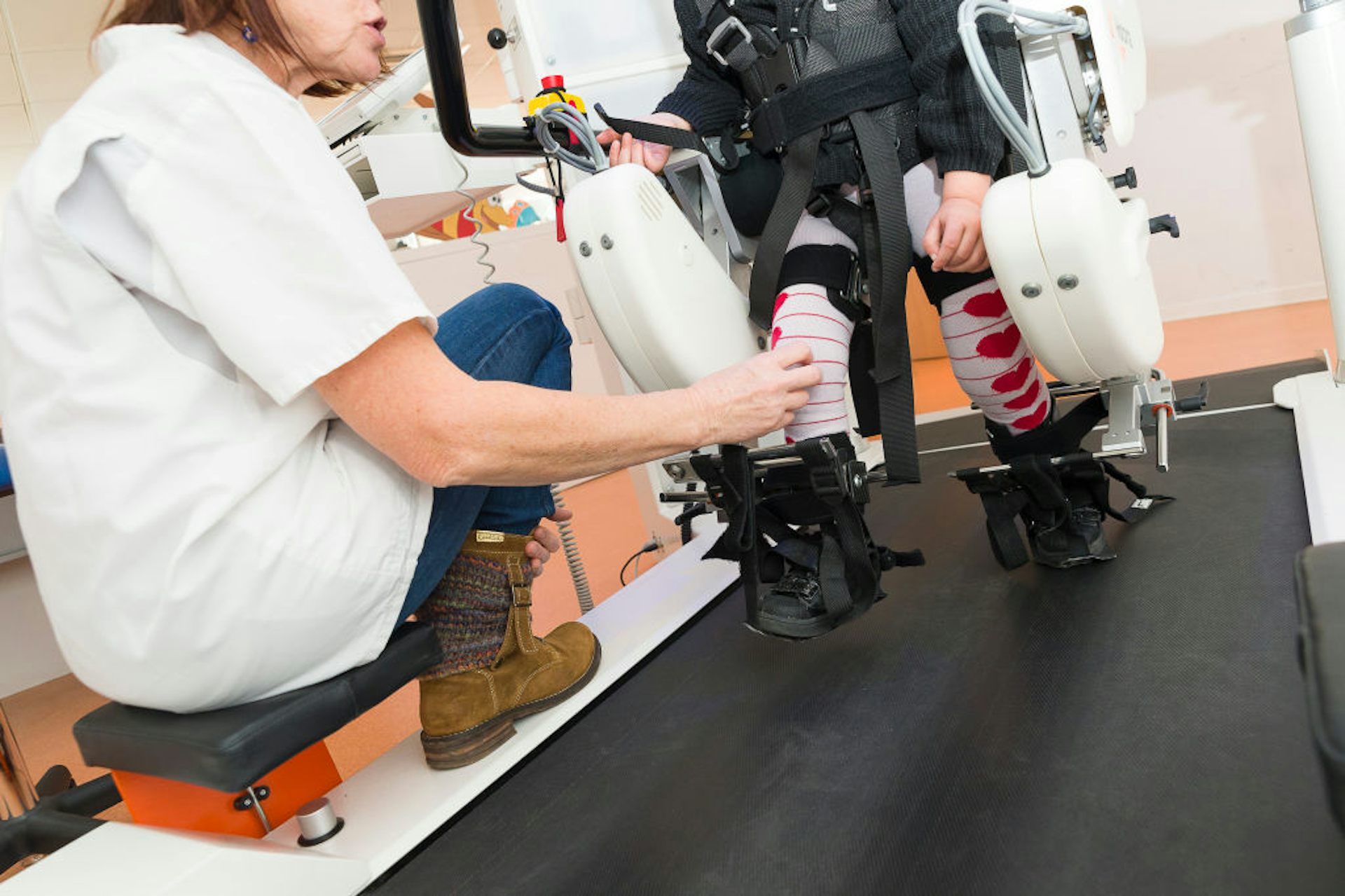

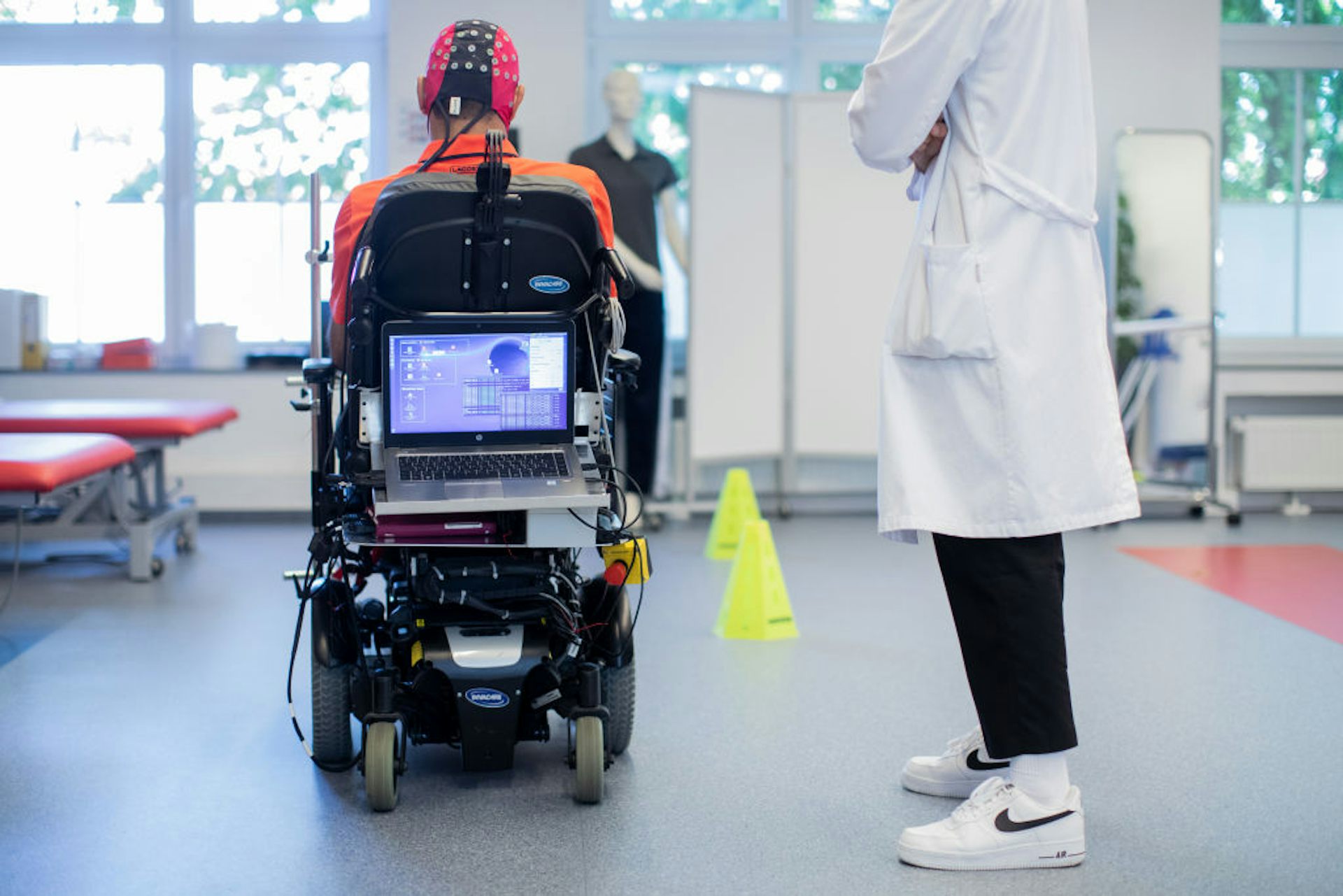
Robotics will help sufferers get better bodily operate in rehabilitation. BSIP/Common Pictures Group by way of Getty Pictures
How individuals talk with robots
Robots had been initially designed to undertake repetitive and mundane tasks and function completely in robot-only zones like factories. Robots have since superior to work collaboratively with individuals with new methods to speak with one another.
Cooperative control is one method to transmit data and messages between a robotic and an individual. It entails combining human skills and determination making with robotic pace, accuracy and energy to perform a process.
For instance, robots within the agriculture industry will help farmers monitor and harvest crops. A human can management a semi-autonomous winery sprayer by way of a consumer interface, versus manually spraying their crops or broadly spraying your complete discipline and risking pesticide overuse.
Robots also can support patients in physical therapy. Sufferers who had a stroke or spinal twine damage can use robots to apply hand greedy and assisted strolling throughout rehabilitation.
One other type of communication, emotional intelligence perception, entails growing robots that adapt their behaviors based mostly on social interactions with people. On this strategy, the robotic detects an individual’s feelings when collaborating on a process, assesses their satisfaction, then modifies and improves its execution based mostly on this suggestions.
For instance, if the robotic detects {that a} bodily remedy affected person is dissatisfied with a selected rehabilitation exercise, it may direct the affected person to an alternate exercise. Facial expression and physique gesture recognition capability are vital design concerns for this strategy. Recent advances in machine learning will help robots decipher emotional physique language and higher work together with and understand people.
Robots in rehab
Questions like methods to make robotic limbs really feel extra pure and able to extra advanced features like typing and enjoying musical devices have but to be answered.
I’m an electrical engineer who research how the mind controls and communicates with different components of the physique, and my lab investigates specifically how the brain and hand coordinate indicators between one another. Our aim is to design applied sciences like prosthetic and wearable robotic exoskeleton devices that would assist enhance operate for people with stroke, spinal twine and traumatic mind accidents.
One strategy is thru brain-computer interfaces, which use mind indicators to speak between robots and people. By accessing a person’s mind indicators and offering focused suggestions, this know-how can probably enhance restoration time in stroke rehabilitation. Mind-computer interfaces can also assist restore some communication abilities and physical manipulation of the environment for sufferers with motor neuron problems.
Mind-computer interfaces may permit individuals to regulate robotic arms by thought alone. Ramana Kumar Vinjamuri, CC BY-ND
The way forward for human-robot interplay
Efficient integration of robots into human life requires balancing accountability between individuals and robots, and designating clear roles for each in several environments.
As robots are more and more working hand in hand with individuals, the moral questions and challenges they pose can’t be ignored. Issues surrounding privacy, bias and discrimination, security risks and robot morality must be severely investigated with a purpose to create a extra comfy, safer and reliable world with robots for everybody. Scientists and engineers learning the “dark side” of human-robot interaction are growing pointers to determine and stop damaging outcomes.
Human-robot interplay has the potential to have an effect on each facet of every day life. It’s the collective accountability of each the designers and the customers to create a human-robot ecosystem that’s secure and passable for all.
![]()
Ramana Vinjamuri receives funding from Nationwide Science Basis.
This text is republished from The Conversation underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the original article.
The Conversation
is an unbiased supply of reports and views, sourced from the tutorial and analysis group and delivered direct to the general public.

The Dialog
is an unbiased supply of reports and views, sourced from the tutorial and analysis group and delivered direct to the general public.
[ad_2]
Source link



