[ad_1]
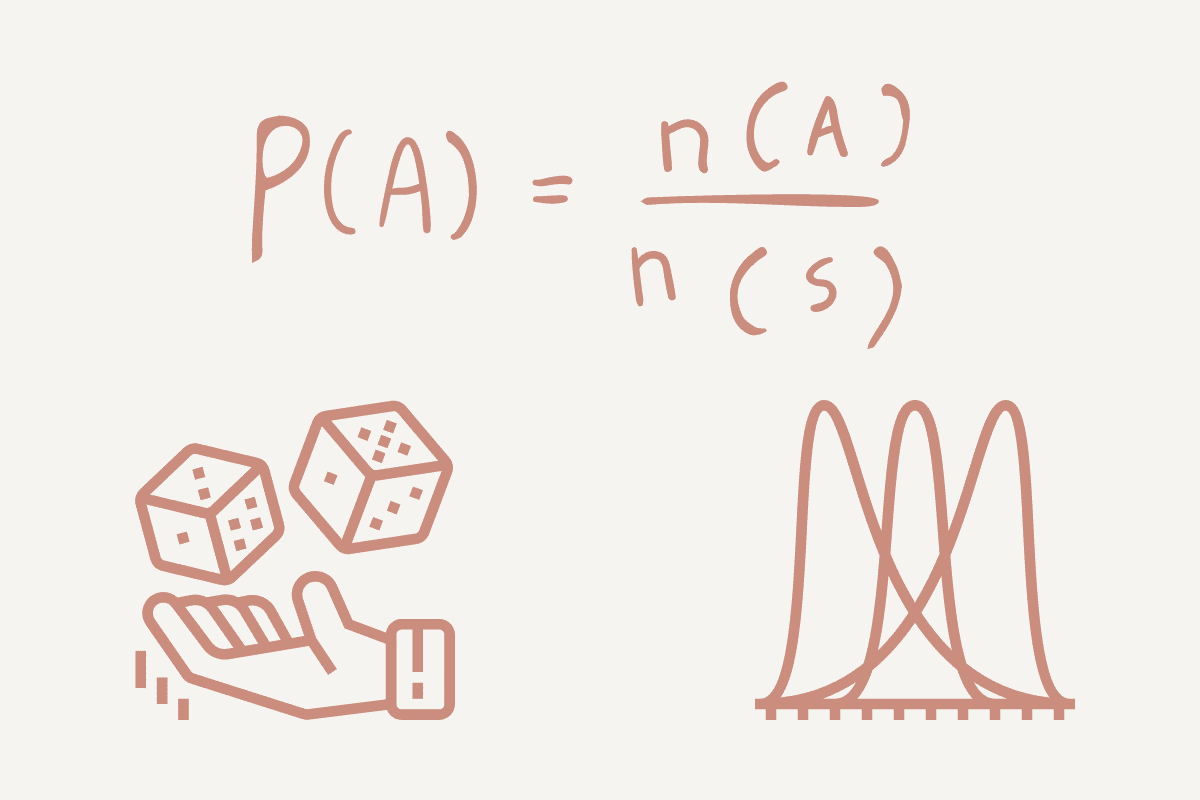
Picture by Creator
As a Knowledge Scientist, you’ll want to know the accuracy of your outcomes to make sure validity. The info science workflow is a deliberate challenge, with managed situations. Permitting you to evaluate every stage and the way it lent in the direction of your output.
Chance is the measure of the chance of an occasion/one thing occurring. It is a vital aspect in predictive evaluation permitting you to discover the computational math behind your consequence.
Utilizing a easy instance, let’s have a look at tossing a coin: both heads (H) or tails (T). Your likelihood would be the variety of methods an occasion can happen divided by the entire variety of attainable outcomes.
- If we need to discover the likelihood of heads, it might be 1 (Head) / 2 (Heads and Tails) = 0.5.
- If we need to discover the likelihood of tails, it might be 1 (Tails) / 2 (Heads and Tails) = 0.5.
However we don’t need to get chance and likelihood confused – there’s a distinction. Chance is the measure of a selected occasion or consequence occurring. Chances are utilized once you need to improve the probabilities of a selected occasion or consequence occurring.
To interrupt it down – likelihood is about attainable outcomes, while chances are about hypotheses.
One other time period to know is ‘’mutually unique occasions’’. These are occasions that don’t happen on the identical time. For instance, you can not go proper and left on the identical time. Or if we’re flipping a coin, we will both get heads or tails, not each.
Varieties of Chance
- Theoretical Chance: this focuses on how probably an occasion is to happen and relies on the muse of reasoning. Utilizing principle, the result is the anticipated worth. Utilizing the top and tails instance, the theoretical likelihood of touchdown on heads is 0.5 or 50%.
- Experimental Chance: this focuses on how often an occasion happens throughout an experiment period. Utilizing the top and tails instance – if we had been to toss a coin 10 occasions and it landed on heads 6 occasions, the experimental likelihood of the coin touchdown on heads can be 6/10 or 60%.
Conditional likelihood is the potential of an occasion/consequence occurring based mostly on an present occasion/consequence. For instance, if you happen to’re working for an insurance coverage firm, it’s possible you’ll need to discover the likelihood of an individual with the ability to pay for his insurance coverage based mostly on the situation that they’ve taken out a home mortgage.
Conditional Chance helps Knowledge Scientists produce extra correct fashions and outputs through the use of different variables within the dataset.
A likelihood distribution is a statistical perform that helps to explain the attainable values and chances for a random variable inside a given vary. The vary can have attainable minimal and most values, and the place they’re plotted on a distribution graph rely on statistical exams.
Relying on the kind of knowledge used within the challenge, you may determine what sort of distribution you’re utilizing. I’ll break them down into two classes: discrete distribution and steady distribution.
Discrete Distribution
Discrete distribution is when the info can solely tackle sure values or has a restricted variety of outcomes. For instance, if you happen to had been to roll a die, your restricted values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6.
There are several types of discrete distribution. For instance:
- Discrete uniform distribution is when all of the outcomes are equally probably. If we use the instance of rolling a six-sided die, there may be an equal likelihood that it may land on 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 – ⅙. Nevertheless, the issue with discrete uniform distribution is that it doesn’t present us with related data, which knowledge scientists can use and apply.
- Bernoulli Distribution is one other sort of discrete distribution, the place the experiment solely has two attainable outcomes, both sure or no, 1 or 2, true or false. This can be utilized when flipping a coin, it’s both head or tails. When utilizing the Bernoulli distribution, we have now the likelihood of one of many outcomes (p) and we will deduct it from the entire likelihood (1), represented as (1-p).
- Binomial Distribution is a sequence of Bernoulli occasions and is the discrete likelihood distribution that may solely produce two attainable ends in an experiment, both success or failure. When flipping a coin, the likelihood of flipping a coin will all the time be 1.5 or ½ in each experiment carried out.
- Poisson Distribution is the distribution of what number of occasions an occasion is more likely to happen over a specified interval or distance. Relatively than specializing in an occasion occurring, it focuses on the frequency of an occasion occurring in a selected interval. For instance, if 12 vehicles go down a specific highway at 11 am each day, we will use Poisson distribution to determine what number of vehicles go down that highway at 11 am in a month.
Steady Distribution
Not like discrete distributions which have finite outcomes, steady distributions have continuum outcomes. These distributions usually seem as a curve or a line on a graph as the info is steady.
- Regular Distribution is one which you will have heard of as it’s the most often used. It’s a symmetrical distribution of the values across the imply, with no skew. The info follows a bell form when plotted, the place the center vary is the imply. For instance, traits equivalent to top, and IQ scores comply with a standard distribution.
- T-Distribution is a sort of steady distribution used when the inhabitants normal deviation (σ) is unknown and the pattern dimension is small (n<30). It follows the identical form as a standard distribution, the bell curve. For instance, if we’re taking a look at what number of chocolate bars had been bought in a day, we’d use the conventional distribution. Nevertheless, if we need to look into what number of had been bought in a selected hour, we’ll use t-distribution.
- Exponential distribution is a sort of steady likelihood distribution that focuses on the period of time until an occasion happens. For instance, we could need to look into earthquakes and might use exponential distribution. The period of time, ranging from this level till an earthquake happens. The exponential distribution is plotted as a curved line and represents the chances exponentially.
From the above, you may see how knowledge scientists can use likelihood to know extra about knowledge and reply questions. It is extremely helpful for knowledge scientists to know and perceive the probabilities of an occasion occurring and will be very efficient within the decision-making course of.
You may be continuously working with knowledge and it’s essential study extra about it earlier than performing any type of evaluation. Wanting on the knowledge distribution can provide you lots of data and might use this to regulate your activity, course of and mannequin to cater to the info distribution.
This reduces your time spent understanding the info, gives a more practical workflow, and produces extra correct outputs.
A whole lot of the ideas of information science are based mostly on the basics of likelihood.
Nisha Arya is a Knowledge Scientist and Freelance Technical Author. She is especially excited about offering Knowledge Science profession recommendation or tutorials and principle based mostly data round Knowledge Science. She additionally needs to discover the other ways Synthetic Intelligence is/can profit the longevity of human life. A eager learner, looking for to broaden her tech data and writing abilities, while serving to information others.
[ad_2]
Source link



